Bipolar disorders affect millions of individuals worldwide, yet it remains one of the most misunderstood mental health conditions. The stigma surrounding bipolar disorder not only isolates those living with the condition but also creates barriers to effective treatment and support. Breaking this stigma is crucial for fostering a more inclusive and supportive environment for those affected.
Understanding the Nature of Stigma
1. What Is Stigma?
Stigma refers to the negative beliefs, attitudes, and stereotypes that society holds about individuals with certain conditions. In the context of bipolar disorder, stigma can take two primary forms:
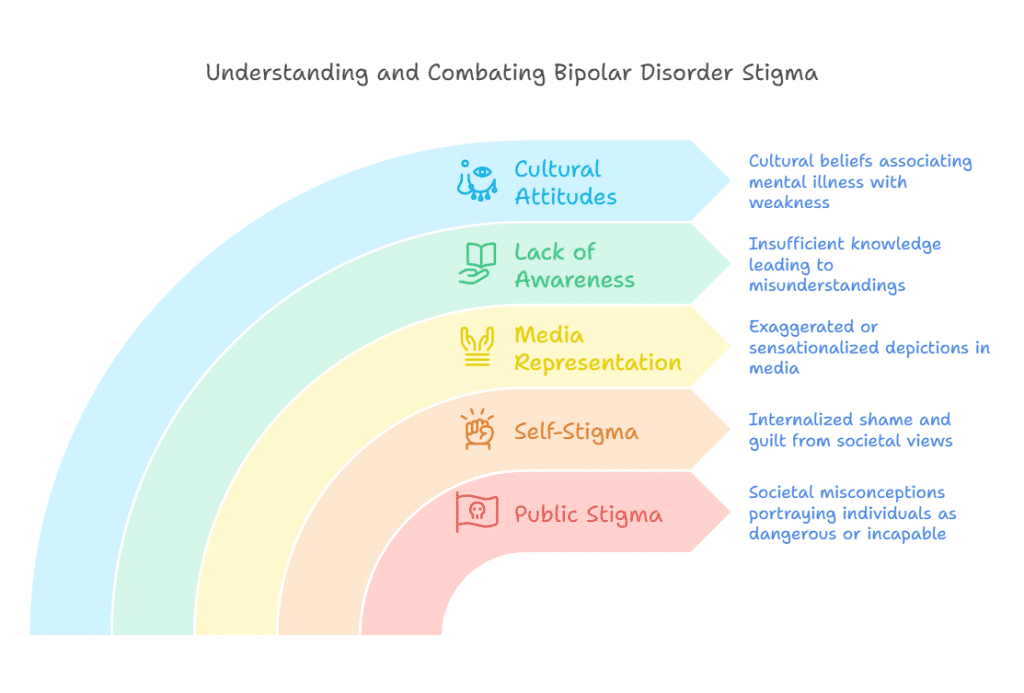
- Public Stigma: Societal misconceptions that portray people with bipolar disorder as unpredictable, dangerous, or incapable of leading fulfilling lives.
- Self-Stigma: Internalized shame and guilt, where individuals with bipolar disorder absorb and accept negative societal views about their condition.
2. Factors Contributing to Stigma:
- Media Representation: Movies, television, and news often depict bipolar disorder in exaggerated or sensationalized ways, reinforcing harmful stereotypes.
- Lack of Awareness: Many people lack accurate knowledge about bipolar disorder, leading to misunderstandings about its symptoms and impact.
- Cultural Attitudes: In some cultures, mental illness is associated with weakness or moral failure, further stigmatizing those with bipolar disorder.
3. Consequences of Stigma:
- Creates an environment where individuals feel judged or discriminated against.
- Discourages open dialogue about mental health, perpetuating misinformation.
- Prevents individuals from seeking help due to fear of being labeled or ostracized.
Impact of Stigma on Mental Health Treatment
1. Barriers to Seeking Help:
Stigma often discourages individuals from pursuing diagnosis or treatment for bipolar disorder. Fear of judgment or discrimination can lead to delays in care, exacerbating symptoms and increasing the risk of complications.
2. Challenges in Adherence to Treatment:
Even after seeking help, individuals may struggle with treatment adherence due to stigma. Self-stigma, in particular, can lead to feelings of hopelessness or doubts about the effectiveness of therapy or medication.
3. Effect on Relationships and Employment:
Stigma can affect personal and professional relationships:
- Social Isolation: Friends and family may withdraw due to misconceptions, leaving individuals without a support system.
- Workplace Discrimination: Employers or colleagues may misunderstand the condition, creating barriers to career advancement or job retention.
4. Amplified Symptoms:
Stigma adds emotional distress, increasing feelings of anxiety, depression, and shame. This additional burden can exacerbate bipolar symptoms, creating a vicious cycle.
Public Awareness and Advocacy Efforts
1. The Role of Awareness Campaigns:
Public education is a powerful tool in combating stigma. Campaigns can dispel myths, educate communities, and encourage empathy. Examples include:
- World Bipolar Day: Celebrated annually to raise awareness and share stories of those living with bipolar disorder.
- Mental Health Month: Broader initiatives that highlight mental health topics, including bipolar disorder.
2. Advocacy Organizations:
Groups like the National Alliance on Mental Illness (NAMI) and the International Bipolar Foundation (IBPF) provide resources, support, and advocacy for those living with bipolar disorder. They promote understanding through public talks, educational materials, and events.
3. The Power of Personal Stories:
Sharing lived experiences can humanize bipolar disorder, challenging stereotypes and fostering empathy. Blogs, podcasts, and social media platforms have become popular avenues for individuals to share their journeys.
4. Media Responsibility:
Encouraging accurate and respectful portrayals of bipolar disorder in film, television, and news can shift public perception. Advocacy groups often work with media creators to ensure authenticity in storytelling.
Steps to Foster a Supportive Environment
1. Education for All:
- Schools: Introduce mental health education into school curricula to foster early understanding and empathy.
- Workplaces: Provide training programs to educate employers and employees about mental health, including bipolar disorder.
- Healthcare Providers: Ensure that medical professionals receive training to recognize and address stigma in clinical settings.
2. Promote Open Conversations:
Creating safe spaces for discussing mental health can normalize these conversations and reduce stigma. Encouraging people to talk about their experiences without fear of judgment fosters a more inclusive environment.
3. Support Networks:
- Peer Support Groups: Connecting with others who have bipolar disorder can provide comfort and shared understanding.
- Family Education Programs: Teaching family members about bipolar disorder helps them provide better support and reduces the likelihood of misunderstanding or discrimination.
4. Challenge Misconceptions:
- Correct misinformation when encountered, whether in casual conversations or online discussions.
- Encourage empathy by emphasizing that bipolar disorder is a medical condition, not a character flaw or personal failing.
5. Encourage Mental Health Policies:
Advocacy efforts should push for legislation that protects individuals with bipolar disorder from
Breaking the stigma surrounding bipolar disorder requires a collective effort involving education, advocacy, and empathy. By understanding the nature of stigma, addressing its impact on mental health treatment, and fostering supportive environments, society can create a culture of acceptance. Through awareness campaigns, personal storytelling, and targeted interventions, we can help those with bipolar disorder lead fulfilling, stigma-free lives. Together, we can change the narrative and promote a future where mental health is treated with the compassion and respect it deserves.





