As the population ages, memory concerns have become increasingly prevalent. While some cognitive decline is a normal part of aging, more significant issues, such as dementia, require specialized care and strategies to improve quality of life. This post explores the types of dementia, lifestyle changes that can enhance memory, and cognitive rehabilitation techniques to support older adults.
Overview of Dementia Types
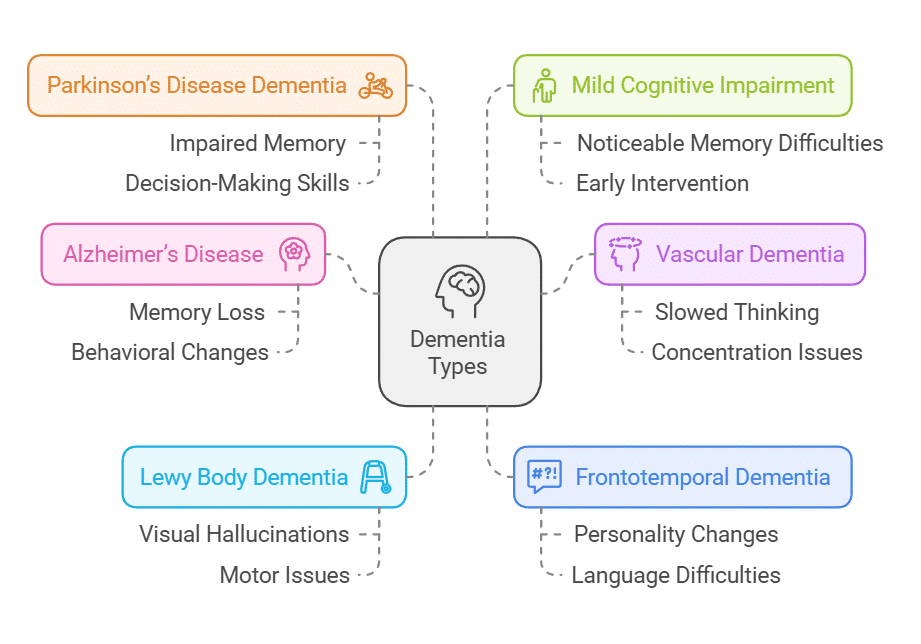
Dementia is a broad term describing a decline in cognitive abilities that interferes with daily life. Understanding the various types of dementia helps tailor effective care and management strategies.
1. Alzheimer’s Disease
Alzheimer’s is the most common form of dementia, accounting for 60-80% of cases. It is characterized by progressive memory loss, difficulties in problem-solving, and behavioral changes. The disease is linked to the accumulation of amyloid plaques and tau tangles in the brain, leading to nerve cell damage.
2. Vascular Dementia
This form of dementia results from impaired blood flow to the brain, often due to strokes or small vessel disease. Symptoms include cognitive impairment, slowed thinking, and difficulty in concentrating. Managing underlying cardiovascular conditions is crucial for treatment.
3. Lewy Body Dementia (LBD)
LBD is associated with abnormal protein deposits in the brain, known as Lewy bodies. It causes symptoms such as visual hallucinations, sleep disturbances, and motor issues similar to Parkinson’s disease. Behavioral symptoms often fluctuate, requiring specialized management.
4. Frontotemporal Dementia (FTD)
FTD primarily affects the frontal and temporal lobes of the brain, leading to personality changes, inappropriate behavior, and language difficulties. Unlike Alzheimer’s, memory may remain intact in the early stages.
5. Parkinson’s Disease Dementia (PDD)
Some individuals with Parkinson’s disease develop cognitive decline at least a year after motor symptoms appear. Symptoms include impaired memory, attention, and decision-making skills.
6. Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI)
MCI is an intermediate stage between normal cognitive aging and dementia. It involves noticeable memory and cognitive difficulties that do not yet interfere significantly with daily life. Early intervention during this stage may slow progression to dementia.
Lifestyle Changes to Enhance Memory
Lifestyle modifications can play a significant role in maintaining and improving cognitive health. These changes are particularly beneficial for individuals with MCI or early-stage dementia.
1. Physical Activity
- Regular exercise, such as walking, swimming, or yoga, promotes blood flow to the brain and stimulates the release of neurotrophic factors that support brain health.
- Strength training and balance exercises reduce the risk of falls, a critical concern for seniors with cognitive impairment.
2. Balanced Diet
- The Mediterranean diet, rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats, has been shown to support brain health and reduce the risk of dementia.
- Specific nutrients, such as omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and vitamins B6, B12, and E, are essential for cognitive functioning.
3. Mental Stimulation
- Activities like puzzles, reading, or learning a new skill stimulate brain activity and help build cognitive reserves.
- Engaging in music therapy or learning to play an instrument enhances memory and mood simultaneously.
4. Quality Sleep
- Poor sleep is linked to cognitive decline. Establishing consistent sleep routines and managing sleep apnea or insomnia can significantly improve memory and cognitive function.
- Techniques such as meditation or relaxation exercises can aid in achieving better sleep quality.
5. Social Engagement
- Staying socially active reduces the risk of depression and loneliness, which are associated with cognitive decline.
- Participating in group activities, volunteering, or connecting with family and friends fosters emotional well-being and cognitive health.
6. Stress Management
- Chronic stress can impair memory and cognitive function. Techniques such as mindfulness, deep breathing, or tai chi help reduce stress levels.
- Therapy or support groups can provide coping mechanisms for stress related to aging and health concerns.
Cognitive Rehabilitation Techniques
Cognitive rehabilitation focuses on helping individuals improve or maintain their cognitive abilities. These techniques are tailored to the specific needs and abilities of older adults, enhancing their independence and quality of life.
1. Memory Training
- Memory exercises involve techniques such as association, visualization, and repetition to improve recall.
- Using mnemonic devices or creating mental maps helps in organizing and retrieving information effectively.
2. Reality Orientation
- Reality orientation therapy helps individuals with dementia stay connected to their environment. It involves reminders about time, place, and current events to reduce confusion.
- Using tools like calendars, clocks, and labeled photographs can support this approach.
3. Cognitive Stimulation Therapy (CST)
- CST involves structured group activities that stimulate thinking, concentration, and memory through games, discussions, and exercises.
- Studies show that CST improves quality of life and cognitive function in individuals with mild to moderate dementia.
4. Assistive Technologies
- Digital tools, such as apps for brain training or devices with voice assistants, can aid memory and daily functioning.
- GPS trackers and medication reminders provide additional support for individuals with advanced cognitive challenges.
5. Occupational Therapy
- Occupational therapists work with individuals to adapt their living environments and develop strategies to perform daily tasks more efficiently.
- Techniques may include simplifying routines, using adaptive tools, or breaking tasks into smaller, manageable steps.
6. Personalized Cognitive Rehabilitation
- Tailored interventions focus on the individual’s strengths and preferences, incorporating meaningful activities that encourage engagement and enjoyment.
- For example, a music-loving individual might use familiar songs to trigger memories or improve mood.
7. Family and Caregiver Involvement
- Training caregivers to support cognitive rehabilitation ensures consistent practice and reinforcement.
- Educating families about effective communication strategies and behavior management enhances care outcomes.
Memory care for older adults is a multifaceted approach involving understanding dementia types, implementing lifestyle changes, and using cognitive rehabilitation techniques. These strategies aim to improve quality of life, maintain independence, and slow cognitive decline. By adopting evidence-based practices and fostering a supportive environment, individuals and caregivers can navigate the challenges of aging with dignity and optimism.
At Amavi Integrative Mental Wellness, we specialize in holistic geriatric psychiatry services that address the unique needs of older adults. Contact us to learn more about our memory care programs and how we can help you or your loved one achieve better mental and cognitive health.





